Your Onan generator isn't just a machine; it's a lifeline. Whether it’s providing crucial backup power during an outage, keeping your RV comfortable on the road, or running essential equipment on a job site, its reliability hinges on the health of its core components. Understanding and properly maintaining your Onan Generator Engine & Cooling System Parts isn't just good practice—it's essential for ensuring that reliable power is always there when you need it most.
This guide dives deep into the heart of your Onan, exploring the vital engine and cooling components that make it tick. We’ll demystify what keeps your generator running smoothly, what to look for when things go wrong, and how to choose the right parts to keep your investment performing optimally for years to come.
At a Glance: Keeping Your Onan Running Strong
- Engine Parts are the Core: From starters to spark plugs, these components ignite, fuel, and power your generator.
- Cooling System Prevents Disaster: Radiators, water pumps, and fans protect your engine from damaging heat.
- Regular Maintenance is Key: Proactive checks and timely part replacements prevent costly breakdowns.
- Genuine Parts Offer Peace of Mind: OEM Onan parts ensure perfect fit, performance, and warranty protection.
- Troubleshooting Saves Time: Knowing common symptoms helps diagnose issues quickly and accurately.
Why Your Onan's Heart (Engine) and Lungs (Cooling) Demand Attention
Onan generators have built a reputation for robust performance and longevity, often becoming trusted companions for decades. But like any complex machinery, their reliable operation depends entirely on the condition of their internal systems. Think of your Onan as a living entity: the engine is its powerful heart, tirelessly converting fuel into electricity, while the cooling system acts as its lungs, regulating temperature to prevent overheating and premature wear.
Neglecting these critical systems is akin to ignoring warning signs in your own health. Small issues can quickly escalate into major failures, leaving you without power precisely when you need it most. Understanding these components empowers you to be a proactive owner, capable of identifying potential problems before they sideline your generator entirely.
The Onan Legacy: Durability Meets Precision
For over 90 years, Onan (now a part of Cummins) has been synonymous with dependable power generation. This isn't by accident. Their generators are engineered with precision, designed to perform under demanding conditions. This legacy means that when you're looking for replacement parts, you're tapping into a history of quality and specific design requirements that generic alternatives simply can't match. Every component, from a tiny gasket to a major engine block, plays a role in upholding that standard.
Understanding the Core: What Makes an Onan Run?
At its simplest, an Onan generator combines an engine (which burns fuel to create mechanical energy) with an alternator (which converts that mechanical energy into electrical power). For the engine to perform its job effectively, it requires several interconnected systems:
- Fuel System: Delivers clean, appropriately mixed fuel to the combustion chamber.
- Ignition System: Creates the spark necessary to ignite that fuel.
- Air System: Ensures a steady supply of clean air for combustion.
- Lubrication System: Keeps moving parts protected from friction and heat.
- Exhaust System: Safely expels combustion byproducts.
- Cooling System: Manages the immense heat generated by combustion and friction.
Each of these systems relies on a network of carefully engineered parts. A single failing component in any of these chains can compromise the entire generator's operation.
Decoding Your Onan Generator's Engine Parts
The engine is the powerhouse of your Onan. It's a marvel of mechanical engineering, where countless parts work in unison to produce the rotational force needed for electricity generation. Knowing these key components helps you understand maintenance needs and diagnose issues more effectively.
The Power Core: Essential Engine Components
Let's break down the critical engine parts you'll encounter and why they matter.
Starters and Solenoids: Getting Things Going
Before your generator can produce power, it needs to start.
- Starter Motor: This electric motor cranks the engine, initiating the combustion cycle. If your generator clicks but doesn't turn over, a failing starter is a prime suspect.
- Solenoid: An electromagnetic switch that engages the starter motor and pushes the starter gear to mesh with the engine's flywheel. A faulty solenoid can prevent the starter from receiving power, leading to a frustrating "no-crank" situation.
Fuel System Components: Clean Fuel, Consistent Power
The fuel system ensures your engine receives the right amount of clean fuel at the right time.
- Fuel Pumps: Whether mechanical or electric, the fuel pump is responsible for drawing fuel from the tank and delivering it under pressure to the carburetor or fuel injectors. A weak or failing pump can lead to fuel starvation, causing your generator to sputter, lose power, or not start at all.
- Fuel Filters: These are your engine's first line of defense against contaminants. They prevent dirt, rust, and debris from reaching sensitive fuel system components, which can cause clogs and damage. Regularly replacing your fuel filter is one of the easiest and most critical maintenance tasks you can perform.
- Carburetors/Injectors:
- Carburetors (for gasoline engines): Mix air and fuel in the correct ratio before sending it to the engine cylinders for combustion. Carburetors can become clogged with old fuel deposits, leading to rough idling, surging, or a complete failure to start.
- Fuel Injectors (for diesel and some newer gasoline engines): Precisely atomize and spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber or intake manifold. They offer better fuel efficiency and emission control but can also become clogged or fail electronically, leading to misfires or poor performance.
Ignition System: Sparking Life
For gasoline engines, the ignition system provides the spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture.
- Spark Plugs: These small but mighty components create the electrical spark inside the combustion chamber. Worn, fouled, or improperly gapped spark plugs can cause misfires, reduced power, increased fuel consumption, and difficult starting.
- Ignition Coils & Modules: The ignition coil transforms the battery's low voltage into the high voltage needed to create a spark. The ignition module (or points/condenser in older models) controls the timing of this spark. Problems here often manifest as intermittent power loss, misfires, or a complete lack of spark.
Air Filtration: Breathing Easy
Just as important as clean fuel is clean air.
- Air Filters: Prevents dust, dirt, and other airborne contaminants from entering the engine. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, causing the engine to run rich (too much fuel, not enough air), leading to reduced power, increased fuel consumption, and potentially carbon buildup.
Belts and Hoses: The Connective Tissue
These flexible components keep fluids flowing and accessories driven.
- Drive Belts: Transmit power from the engine to accessories like the alternator, water pump (in some designs), or cooling fan. A worn, cracked, or loose belt can slip, causing underperformance of the driven component, or break, leading to immediate system failure.
- Engine Hoses: Carry vital fluids like fuel, oil, and coolant. Hoses can degrade over time due to heat, pressure, and chemical exposure, leading to leaks. Inspect them for cracks, bulges, and softness regularly.
Exhaust System: Quiet and Clean Operation
The exhaust system manages combustion byproducts.
- Mufflers and Gaskets: The muffler reduces engine noise, while exhaust gaskets seal connections to prevent leaks. A leaking exhaust system can lead to dangerous carbon monoxide buildup, excessive noise, and reduced engine efficiency.
Common Engine Part Wear & Tear: What to Watch For
Regular inspection of your Shop Onan generator parts can save you significant headaches and costs down the line. Here are some tell-tale signs of common engine issues:
- Starting Problems:
- No Crank: Could be a dead battery, faulty starter motor, or solenoid.
- Cranks but No Start: Often points to issues with fuel delivery (empty tank, clogged filter, bad pump), ignition (no spark, bad spark plugs/coil), or air (clogged air filter).
- Rough Running/Misfires: The engine sounds uneven, shakes excessively, or loses power under load. This can stem from fouled spark plugs, dirty fuel injectors/carburetor, incorrect fuel mixture, or air leaks.
- Unusual Noises or Vibrations: Any new knocking, clunking, or squealing sounds should be investigated immediately. These could indicate serious internal engine wear, loose belts, or failing bearings.
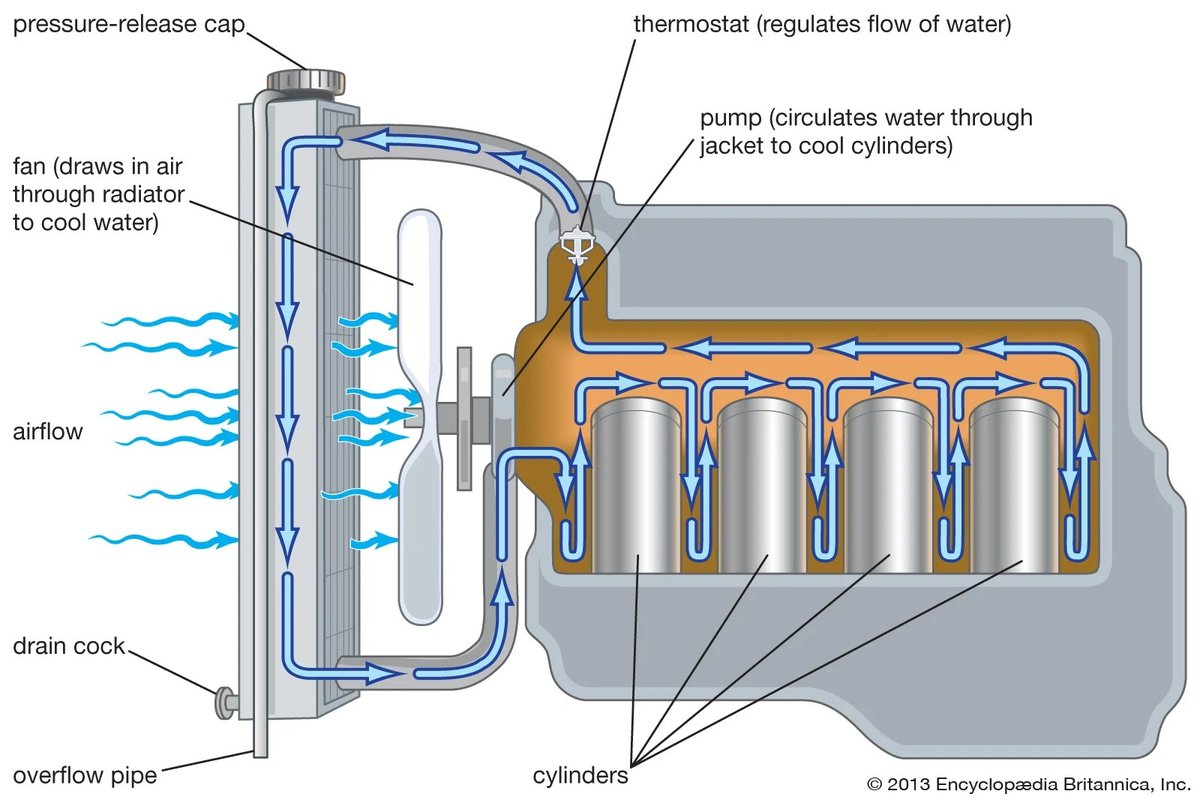
The Crucial Role of Your Onan's Cooling System
An Onan engine generates a tremendous amount of heat. If this heat isn't efficiently dissipated, the engine will overheat, leading to catastrophic damage like warped cylinder heads, blown head gaskets, or seized pistons. The cooling system is your generator's critical defense against thermal destruction.
Keeping the Heat in Check: Core Cooling Components
Understanding each part of the cooling system helps you identify weak links.
Radiators and Heat Exchangers: The Ultimate Coolers
- Radiator (air-cooled engines): Air is drawn through fins to cool circulating coolant. Blocked fins from dirt or debris severely impede cooling efficiency.
- Heat Exchanger (liquid-cooled engines, often marine or commercial): Transfers heat from the engine coolant to a secondary cooling medium, often raw water or a separate closed-loop coolant system. These need to be kept clean to ensure efficient heat transfer.
Water Pumps: Circulating Lifeblood
The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine block, cylinder head, and radiator. It’s driven by a belt or gears and is essential for maintaining a consistent flow of coolant. A failing water pump (indicated by leaks, grinding noises, or a rapidly rising temperature gauge) will quickly lead to overheating.
Thermostats: Temperature Regulators
The thermostat is a temperature-sensitive valve that regulates coolant flow to the radiator. When the engine is cold, it remains closed to help the engine warm up quickly. Once the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature, the thermostat opens to allow coolant to circulate through the radiator. A stuck-closed thermostat will cause immediate overheating; a stuck-open one will prevent the engine from reaching optimal operating temperature, leading to reduced efficiency.
Coolant Hoses and Clamps: Leak-Free Circulation
High-pressure, high-temperature hoses connect various components of the cooling system. Over time, these hoses can harden, soften, crack, or leak. Clamps secure the hoses, and if they corrode or loosen, they can also cause leaks. Regular inspection is key.
Coolant (Antifreeze): More Than Just Water
Coolant is a mixture of antifreeze (ethylene glycol or propylene glycol) and water. It performs several vital functions:
- Heat Transfer: Efficiently absorbs and dissipates heat.
- Freeze Protection: Prevents the cooling system from freezing in cold weather.
- Corrosion Protection: Contains additives that protect engine components from rust and corrosion.
- Lubrication: Lubricates the water pump.
Using the correct type and concentration of coolant specified by Onan/Cummins is crucial.
Fans and Fan Motors: Airflow Essentials
- Cooling Fan: Draws air through the radiator to enhance heat dissipation. It can be belt-driven or electrically driven.
- Fan Motor (for electric fans): Powers the cooling fan. A failing fan motor or a broken fan blade will drastically reduce cooling capacity, leading to overheating.
Temperature Sensors: The System's Eyes and Ears
Temperature sensors monitor the engine and coolant temperatures, providing data to the generator's control system. This information is used to trigger alarms, shut down the generator in case of overheating, or activate the cooling fan. A faulty sensor can provide inaccurate readings, leading to false alarms or, worse, failure to detect a real overheating situation.
Recognizing Cooling System Distress Signals
Being vigilant about these signs can prevent engine damage.
- Overheating: The most obvious sign. Your generator's temperature gauge rising into the red, or an overheating alarm, demands immediate attention. This can indicate a low coolant level, a faulty thermostat, a failing water pump, a blocked radiator, or a non-functional fan.
- Coolant Leaks: Puddles under your generator, rust-colored stains, or a noticeable drop in coolant level all point to a leak. Common culprits include cracked hoses, loose clamps, a leaking radiator, or a failing water pump seal.
- Inconsistent Temperatures: The temperature gauge fluctuating wildly can indicate a sticking thermostat or a problem with the temperature sensor itself.
- Fan Not Engaging: If your electric cooling fan doesn't turn on when the engine gets hot, it could be a faulty fan motor, a blown fuse, or a bad temperature sensor.
The Right Part, The First Time: Choosing Genuine Onan Components
When it comes to maintaining your Onan generator, choosing the right parts is paramount. It’s not just about a temporary fix; it’s about long-term reliability and performance.
Why OEM Matters: A Case for Quality and Fit
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are identical to the components originally installed in your Onan generator. They are designed, tested, and approved by Cummins (Onan's parent company) to meet precise specifications for fit, form, and function.
- Guaranteed Fit: OEM parts are engineered to fit perfectly, ensuring easy installation and preventing strain on other components.
- Optimal Performance: They're designed to work synergistically with your specific Onan model, maintaining peak efficiency and power output.
- Reliability & Durability: OEM parts are made from high-quality materials and subjected to rigorous testing, offering superior longevity compared to many aftermarket alternatives.
- Warranty Protection: Using genuine Onan parts often maintains your generator’s warranty, whereas aftermarket parts could potentially void it.
While aftermarket parts might sometimes be cheaper upfront, the risks—poor fit, premature failure, reduced performance, and potential damage to other components—can lead to higher costs and frustration in the long run.
Avoiding Counterfeit Parts: Risks and Consequences
The market, unfortunately, also features counterfeit parts. These are often low-quality imitations passed off as genuine Onan products. They pose significant risks:
- Safety Hazards: Counterfeit parts can fail unexpectedly, leading to fires, explosions, or mechanical breakdowns.
- Catastrophic Damage: A critical counterfeit component failure can cause severe, irreparable damage to your entire engine or cooling system.
- Voided Warranty: Using non-genuine parts will almost certainly void any existing manufacturer's warranty.
- Poor Performance: They simply won't perform to Onan's standards, leading to reduced efficiency, increased fuel consumption, and unreliable power.
Decoding Part Numbers and Serial Plates: Your Guide to Accuracy
To ensure you're getting the correct genuine Onan parts, you need accurate information.
- Generator Model and Spec Number: This is usually found on a data plate directly on your generator. The spec letter (e.g., A, B, C) is particularly important as Onan often makes running changes within a model series.
- Part Numbers: If you're replacing an existing part, the part number is often stamped directly on the component.
- Serial Number: Crucial for Onan to identify the exact build configuration of your unit.
When searching for parts, always provide your supplier with your generator's full model and spec number. This eliminates guesswork and ensures you get the exact components needed. When you’re ready to source new components, you can Shop Onan generator parts from reputable distributors that specialize in genuine products.
Maintenance Mastery: Extending the Life of Your Onan
Proactive maintenance is the single most effective way to ensure your Onan generator provides reliable power for years. It's about preventing problems before they start, rather than reacting to failures.
Routine Engine Checks: Your Preventative Toolkit
Think of these as your generator's regular check-up.
- Oil Changes and Filter Replacements: Engine oil lubricates moving parts and dissipates heat. Over time, it breaks down and accumulates contaminants. Follow Onan's recommended service intervals for oil and oil filter changes (often every 50-200 hours of operation or annually, whichever comes first). Using the correct oil type and weight is critical.
- Spark Plug Inspection and Replacement: For gasoline engines, inspect spark plugs for fouling, wear, and correct gap. Replace them according to the maintenance schedule or if they show signs of wear.
- Fuel Filter Service: Replace fuel filters at recommended intervals. This is a small investment that prevents big problems down the line from contaminated fuel.
- Air Filter Cleaning/Replacement: Check your air filter regularly, especially in dusty environments. Clean or replace it when it appears dirty or clogged to ensure proper airflow and fuel-air mixture.
- Belt Tension and Condition Checks: Inspect all drive belts for cracks, fraying, and proper tension. A loose belt can slip, leading to reduced efficiency, while a worn belt can break, causing immediate component failure.
Cooling System Care: Preventing Meltdowns
The cooling system requires dedicated attention to avoid overheating.
- Coolant Level and Condition Checks: Regularly check the coolant level in the overflow reservoir and, when cold, in the radiator itself. Top up with the correct coolant mixture. Also, observe the coolant's color and clarity; a rusty, sludgy, or oily appearance can indicate internal issues.
- Hose and Clamp Inspections: Physically inspect all cooling system hoses for signs of cracking, bulging, softness, or hardening. Check all hose clamps for corrosion and tightness. Replace any suspicious hoses or clamps immediately.
- Radiator/Heat Exchanger Cleaning: Ensure the radiator fins or heat exchanger tubes are free from dirt, debris, leaves, and insects. A blockage here can severely restrict airflow and heat transfer. Use a soft brush or compressed air to clean them carefully.
- Fan Functionality Test: For electric fans, ensure they cycle on and off as designed when the engine warms up. Check the fan blades for any damage.
- Thermostat Testing (if troubleshooting): While not a routine check, if you suspect a thermostat issue, it can be tested by observing engine warm-up patterns or, in some cases, by immersing it in heated water.
Storage and Seasonal Considerations
How you store and prepare your Onan can significantly impact its longevity.
- Winterizing Your Onan: If you live in a cold climate, ensure your cooling system has the correct antifreeze concentration. Also, stabilize the fuel or drain it to prevent gumming and varnish in the fuel system.
- Preparing for Peak Usage: Before hurricane season, camping trips, or major events, perform all routine maintenance checks to ensure your Onan is ready for continuous, reliable operation. Don't forget to Shop Onan generator parts for any items you need to replace.
Troubleshooting Common Onan Engine & Cooling System Issues
When your Onan acts up, a systematic approach to troubleshooting can save you time and money.
My Generator Won't Start: A Step-by-Step Diagnostic
- Check the Basics: Is there fuel in the tank? Is the fuel valve open? Is the battery charged? Are the spark plug wires connected (gasoline models)?
- Does it Crank?
- No Crank (just a click or nothing): Check battery terminals, main fuses, starter solenoid, and starter motor.
- Crank but No Start:
- Fuel Issues: Is the fuel filter clogged? Is the fuel pump working? Is the carburetor or injectors clean?
- Ignition Issues (gasoline): Are the spark plugs good? Is there spark at the plugs? Is the ignition coil/module working?
- Air Issues: Is the air filter severely clogged?
- Check Safety Shutoffs: Many Onan generators have low oil pressure or high temperature shutoffs. Ensure oil level is correct and temperature is not excessively high.
It's Running, But Not Producing Power: (A Quick Note on Engine Health)
While not strictly an engine part issue, a generator producing no power (or unstable power) can sometimes indirectly stem from engine problems like severe misfires or low RPMs, which can prevent the alternator from properly generating electricity. Ensure the engine is running smoothly and at its rated RPM.
The Overheating Alarm Keeps Tripping: What to Check First
This is a critical warning; prolonged overheating can destroy your engine.
- Check Coolant Level: The simplest cause is often low coolant.
- Inspect Radiator/Heat Exchanger: Is it clogged with debris? Are the fins bent?
- Check Cooling Fan: Is it running? Are the blades intact?
- Inspect Hoses and Clamps: Look for leaks or collapsed hoses.
- Feel Radiator Hoses: Is the top hose hot and the bottom hose significantly cooler? If both are hot, the thermostat might be stuck closed. If both are cold, the water pump might not be circulating coolant.
- Consider Thermostat/Water Pump: If external checks yield nothing, the thermostat or water pump may be failing internally.
Why is My Coolant Disappearing?
A mysterious drop in coolant usually indicates a leak.
- External Leaks: Thoroughly inspect all hoses, clamps, the radiator/heat exchanger, and the water pump for visible drips or stains. A pressure test can help pinpoint elusive leaks.
- Internal Leaks: If there are no external leaks, the coolant might be leaking internally. This could be a blown head gasket, a cracked cylinder head or block. Signs include white smoke from the exhaust (steam), oil in the coolant (milky appearance), or coolant in the oil (milky oil on the dipstick). These are serious issues requiring professional diagnosis.
For any specific parts, remember to refer to your generator's manual or visit a trusted supplier where you can Shop Onan generator parts that are guaranteed to fit your model.
Your Power Playbook: Next Steps for Onan Reliability
Maintaining your Onan generator’s engine and cooling system isn't just a chore; it's an investment in uninterrupted power and peace of mind. By understanding the critical components, adhering to a diligent maintenance schedule, and knowing how to troubleshoot common issues, you empower yourself to keep your generator running reliably for years to come.
Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
The information in this guide provides a solid foundation. Continue to consult your specific Onan generator's owner's manual for precise maintenance schedules, fluid specifications, and troubleshooting steps tailored to your model. Education is your best tool against unexpected power failures.
The Value of Professional Service (When to Call in the Pros)
While many routine maintenance tasks and basic troubleshooting steps are well within the capabilities of a dedicated owner, some complex issues demand professional expertise. If you're dealing with:
- Persistent overheating despite basic checks.
- Major engine noises or performance issues.
- Suspected internal engine or cooling system leaks.
- Electrical control system malfunctions.
- Any repair that makes you uncomfortable or requires specialized tools.
Don't hesitate to contact a certified Onan/Cummins service technician. Their experience and diagnostic equipment can pinpoint problems quickly and ensure repairs are done correctly, using genuine parts.
Investing in Longevity: Making Smart Part Choices
The longevity and reliability of your Onan generator ultimately depend on the quality of its components. Always prioritize genuine Onan parts to ensure compatibility, performance, and durability. Whether it's a new fuel filter, a replacement water pump, or a set of spark plugs, choosing OEM quality ensures your generator can continue to deliver the dependable power you rely on.
Ready to secure the best for your Onan? Take the next step in ensuring your generator's peak performance and longevity. Shop Onan generator parts from a trusted source today and keep your power flowing, no matter what.